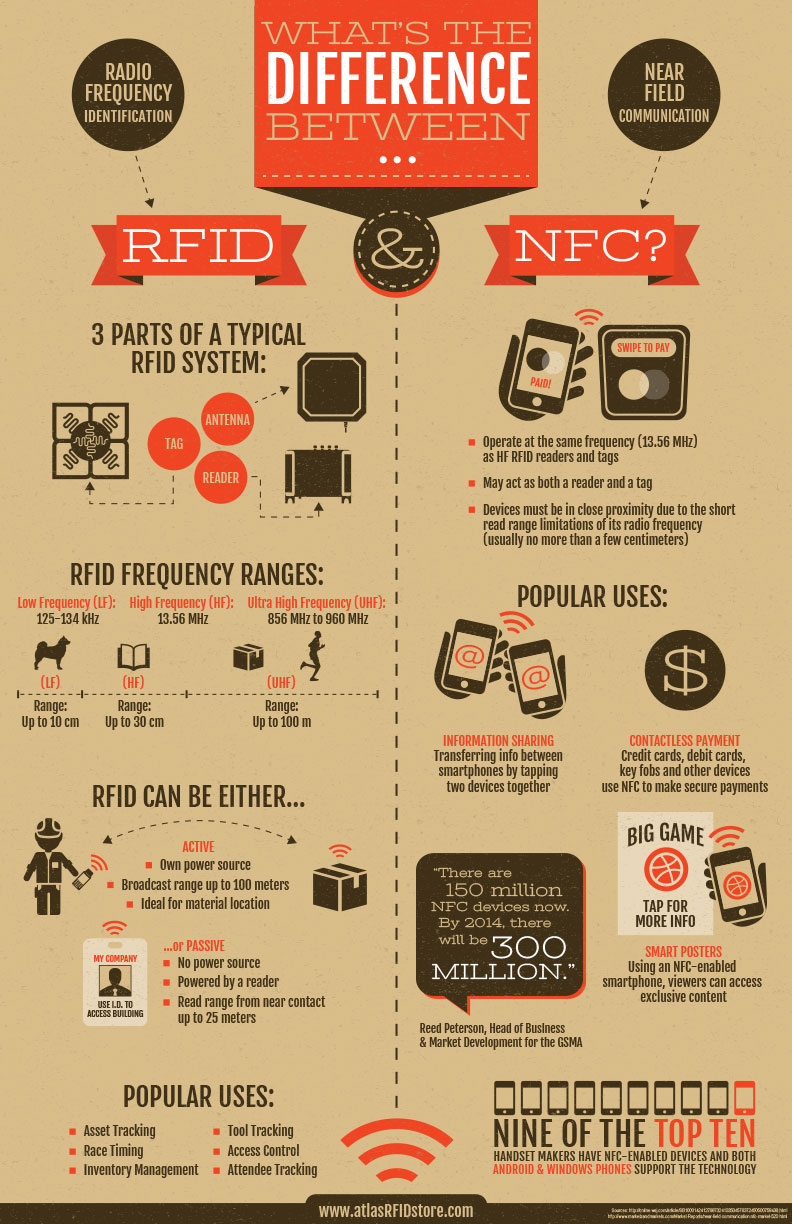
- 125 Khz (low-frequency) tags are write-once/read-many, and usually only contain a small (permanent) unique identification number.
- 13.56 Mhz (high-frequency) tags are usually read/write, they can typically store about 1 to 2 kilbytes of data in addition to their preset (permanent) unique ID number.
- 860-960 Mhz (ultra-high-frequency) tags are typically read/write and can have much larger information storage capacity (I think that 64 KB is the highest currently available for passive tags) in addition to their preset (permanent) unique ID number.
Most read/write tags can be locked to prevent further writing to specific data-blocks in the tag’s internal memory, while leaving other blocks unlocked. Different tag manufacturers make their tags differently, though.
Depending on your intended application, you might have to program your own microcontroller to interface with an embedded RFID read/write module using a manufacturer-specific protocol.
 Home
Home